Pronoun Cases
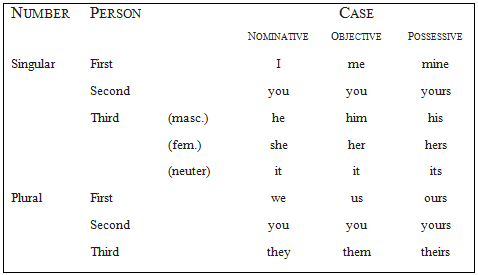
The following chart helps us to sort out the three personal pronoun cases: (1) If a pronoun is a subject or predicate nominative, it is nominative case. (2) A pronoun used as a direct object, indirect object, or object of a preposition is objective case. (3) If a pronoun shows possession, it is possessive case.
Example 1
Identify pronoun cases. Tell whether each italicized pronoun is nominative, objective, or possessive case.
- Mia, Rene, and she giggled.
- Arturo believes her.
- Yours is on the table.
- Mariya tickled her.
- Larry, Gary, and he built the doghouse.
- Mary put him in the doghouse.
- His is the biggest dog dish.
- Gouverneur Morris and he represented the commercial Federalists.
- Congress gave him authority over the disordered finances of the new nation.
- His was the largest contribution.
Solutions
We name pronoun cases:
- nominative case
- objective case
- possessive case
- objective case
- nominative case
- objective case
- possessive case
- nominative case
- objective case
- possessive case
The pronoun case depends on how the pronoun is used in the sentence. We refer to the chart to decide which pronoun is correct for this sentence:
(We, Us) drummers will set the tempo.
The pronoun we identifies "drummers," which is the subject of the sentence. We use the nominative case pronoun we (NOT us) as a subject. Therefore, we write:
We drummers will set the tempo.
Example 2
To identify pronoun cases, tell how the pronoun is used in each sentence (subject, direct object, indirect object, object of a preposition, or possession).
- Ms. Hoo thanked him for the gift.
- That car is hers.
- We promised to help.
- Shawn gave her a broom.
- Mia and Minh laughed with them.
- We served Kristina another helping.
- Boomer likes him for building a doghouse.
- They found themselves "in the doghouse" because they were late to dinner.
- Boomer growled at them for trying to crawl into his house.
- He gave her a lick for filling his dish with meat.
- They agreed with Robert Morris's suggestion for paying war debts.
- Morris had argued with them over debt payment.
Solutions
- Him is a direct object.
- Hers shows possession.
- We is the subject.
- Her is an indirect object.
- Them is an object of a preposition.
- We is the subject.
- Him is a direct object.
- They is the subject.
- Them is an object of a preposition.
- Her is an indirect object.
- They is the subject.
- Them is the object of the preposition "with."
Example 3
Determine how the pronoun is used in each sentence. Then refer to the pronoun cases chart above to help you choose the correct pronoun. Rewrite each sentence correctly.
- The class elected Yiwen and (he, him).
- Both Henry and (she, her) have arrived.
- The invitation was sent to Donald and (she, her).
- Mr. Mango won stuffed animals for Miss Grape and (she, her).
- The fair bored Miss Prune and (he, him).
- Both John Dickinson and (he, him) opposed the Declaration of Independence, yet Robert Morris signed it.
- Robert Morris provided funds for Washington's army and (they, them).
- The war profited Charles Willing and (he, him).
Solutions
1. The pronoun is a direct object, so we choose the objective case pronoun him.
- The class elected Yiwen and him.
2. The pronoun is the subject of the sentence, so we choose the nominative case pronoun she.
- Both Henry and she have arrived.
3. The pronoun is an object of the preposition to, so we choose the objective case pronoun her.
- The invitation was sent to Donald and her.
4. The pronoun is the object of the preposition "for," so we choose the objective case pronoun her.
- Mr. Mango won stuffed animals for Miss Grape and her.
5. The pronoun is a direct object, so we choose the objective case pronoun him.
- The fair bored Miss Prune and him.
6. The pronoun is a sentence subject, so we choose the nominative case pronoun he.
- Both John Dickinson and he opposed the Declaration of Independence, yet Robert Morris signed it.
7. The pronoun is the object of the preposition "for," so we choose the objective case pronoun them.
- Robert Morris provided funds for Washington's army and them.
8. The pronoun is a direct object, so we choose the objective case pronoun him.
- The war profited Charles Willing and him.