Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time modify a verb to tell "when." Let's think about when Lucy skates, when the President dresses, and when Charles Pinckney served:
Lucy skates often.
She might also skate daily, weekly, or hourly.
The President dresses early.
He might also dress later, soon, or nightly.
Charles Pinckney served daily.
He might also have served today, then, or monthly.
Here are some common adverbs of time, telling "when."
|
after |
daily |
nightly |
tomorrow |
Adverb Position
An adverb usually appears near the verb it modifies.
Abe will soon leave for home.
Abe will leave soon for home.
But adverbs of time can appear almost anywhere in a sentence.
Soon Abe will leave for home.
Abe will leave for home soon.
Even though the adverb soon modifies the verb leave in each of the sentences above, it is not necessarily placed near the verb. Since the placement of the adverb can vary, we must learn to identify adverbs even when they are separated from the verbs they modify.
Examples 1
For each sentence, write the adverb that tells "when" and the verb or verb phrase it modifies.
- Fido sometimes eats avocados.
- Tomorrow he will learn the answer.
- Perkins always sleeps late on weekends.
- Why did Jeremy leave the performance early?
- Salem, Massachusetts, was then a leading seaport in the United States.
- Hawthorne worked daily on his best novel, The Scarlet Letter.
- Eventually, Nathaniel Hawthorne married his sweetheart, Sophia Peabody.
- Abraham Baldwin is now remembered as an outstanding teacher at Yale University.
- Baldwin had served as chaplain in the American army before.
- Later, he effected the compromises on slavery and equal representation in the Senate.
- He finally embraced Southern attitudes and political beliefs.
Solutions
- The adverb sometimes modifies the verb eats.
- The adverb tomorrow tells "when" he will learn. Tomorrow modifies the verb phrase will learn.
- The adverb always modifies the verb sleeps.
- The adverb early modifies the verb phrase did leave.
- The adverb then tells "when" Salem was a leading seaport. Then modifies the verb was.
- The adverb daily modifies the verb worked.
- The adverb eventually modifies the verb married.
- The adverb now tells "when" Abraham Baldwin is remembered as an outstanding teacher. Now modifies the verb is remembered.
- The adverb before modifies the verb had served.
- The adverb later modifies the verb effected.
- The adverb finally modifies the verb embraced.
Examples 2
Diagram these sentences:
- My grandparents exercise daily.
- Will you write a novel soon?
- Shall we discuss politics today?
Solutions
1. We place the adverb daily under the verb exercise:
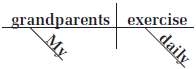
2. We place the adverb soon under the verb will write:

3. We place the adverb today under the verb shall discuss:
